Introduction
Entrepreneurship is the process by which individuals pursue opportunities without regard to the resources they currently control (Stevenson’s 1983). Richard Cantillon (circa 1730) says that, Entrepreneurship is defined as self-employment of any sort. Entrepreneurs buy at certain prices in the present and sell at uncertain prices in the future. The entrepreneur is a bearer of uncertainty. Jean Baptiste (1816) state that the entrepreneur is the agent “who unites all means of production and who finds in the value of the products…the reestablishment of the entire capital he employs, and the value of the wages, the interest, and rent which he pays, as well as profits belonging to himself.”
Task 1 Explore and illustrate the range of venture types that might be considered entrepreneurial
P1 Examine different types of entrepreneurial ventures and explain how they relate to the typology of entrepreneurship.
Entrepreneurship refers to the concept of developing and managing a business venture in order to gain profit by taking several risks in the corporate world.
Types of entrepreneurial ventures:
• Entrepreneurs
• Serial entrepreneurs
• Intrapreneur
• Owner Manager
Entrepreneurs
The term” entrepreneur” is derived from the French verb ‘enterprenedre’. It means “to undertake”. An entrepreneur is a person who undertakes and operates a new enterprise or venture and assumes some accountability for the inherent risks. The term “entrepreneur” was applied to business initially by the French economist, Cantillon, in the 18th century, to designate a dealer who purchases the means of production form combining them into marketable products.
Serial entrepreneurs
A serial entrepreneur is someone who starts and leads one business after another or, multiple businesses at the same time. This is opposed to an entrepreneur who starts a single business and runs the day-to-day operations of that business until exit or retirement. (Griffiths, 2013)
Intrapreneurs:
Of late a new breed of corporate entrepreneurs has come to the force in large organizations are called as “intrapreneurs”. They are entrepreneurs who catch hold of a new idea for a product, service, or process and work to bring this idea to fruition within the framework of the organization. Intrapreneurs with their innovations and dedicated effort are perceived as a valuable asset by the organization, inspiring others.
Difference between Entrepreneur and Intrapreneur
1. Dependency
An entrepreneur is independent
An intrapreneur is dependent on the entrepreneur.
2. Raising of funds
Entrepreneurs: They can raise fund required for the enterprise
Intrapreneurs: Funds are not raised
3. Risk
Entrepreneurs: He/She bears the risk involved in the business
An intrapreneur does not fully bear the risk
4. Operations
Entrepreneurs: He/She operates from outside
Intrapreneurs: He/She operates from within the organization itself
Owner Manager
This is a person who establishes and manages an enterprise for the principal purpose of furthering his or her personal goals. The enterprise is the primary source of income and consumes the majority of the owner-manager’s time and resources. She or he exercises significant control over the day-to-day operations of his or her business.
Distinction between an Entrepreneur and a Manager
Factors
Entrepreneur
Manager
1. Motive
The main motive is to start a venture by setting up an enterprise. He understands the venture for his personal gratification.
The main motive of a manager is to render his services in an enterprise already set up by someone else
2.Status
He is the owner of enterprise
A manger is the servant in the enterprise owned by the entrepreneur
3. Risk bearing
He being the owner of the enterprise assumes all risks and uncertainty involved in running the enterprise
A manager as a servant does not bear any risk involved in the enterprise
4. Rewards
The reward that he gets for bearing risks involved in the enterprise is profit which is highly uncertain
A manager gets salary as reward for the services rendered by him in the enterprise, which is fixed and certain
5. Innovation
He himself thinks over what and how to produce goods to meet then changing demands of the customers. Hence, he acts as an innovator also called a change agent
Manager simply executes the plan prepared by the entrepreneur and translates the entrepreneur’s ideas into practice.
Entrepreneurial activities
The entrepreneur is always a speculator. He deals with the uncertain conditions of the future. His success or failure depends on the correctness of his anticipation of uncertain events. If he fails in his understanding of things to come he is doomed…
(von Mises, 1949/1996)
P2 Explore the similarities and differences between entrepreneurial ventures.
“Entrepreneurship is the ability to recognize the bigger picture, find where there’s an opportunity to make someone’s life better, design hypotheses around these opportunities, and continually test your assumptions. It’s experimentation: Some experiments will work; many others will fail. It is not big exits, huge net worth or living a life of glamour. It’s hard work and persistence to leave the world a better place once your time here is done.” – Konrad Billetz, CEO of Frameri
For a better understanding of the similarities and differences between entrepreneurial ventures the following chart will be useful.
Type of firm: Small Business
Definition: An independently-owned and -operated for-profit enterprise that is not dominant in its field
Goal: Grow into a long-term business that is profitable and sustainable, with possibility of eventual sale to an employee or hand over to a family member
Kind of Business: Restaurants; retail stores; construction firms; agriculture
Capital Providers: Micro-loans; bank loans; revenue; friends, family and personal funds
Outcomes: Small businesses can generate payroll taxes and jobs, but are not large employers. They provide products and services that are necessary parts of a city’s infrastructure, as well as leisure goods and retail. Type of Firm: Scalable Startup (Innovation-Led or High Growth Tech Company)
Definition: Young, innovation-focused firms with the potential to create a new market or dramatically change an existing market via proprietary, technology-based products or services
Goal: Company is built to scale with the goal of generating significant wealth for founder and investors, either through an acquisition or an IPO
Kind of Business: A company producing medical devices or developing life-saving medicine; IT companies developing B2B software or apps; cleantech-geared firms
Capital Providers: Risk capital (accelerators, venture capital, angel investment); non-dilutive capital (government grants, SBIR/STTR); friends, family and personal funds
Outcomes: Startups have the potential to create significant revenue, jobs and economic impact.
Type of Firm: Large Business
Definition: An established firm that employs at least 500 people
Goal: Generating substantial revenue and profit for the company and its shareholders Kind of Business: Corporations (e.g., General Electric, AT&T, General Motors) Capital Providers: Revenue; tax credits; subsidiaries
Outcomes: Large companies are a significant employer in the community. Tend to be recognizable anchors/major brands with an established reputation and community presence Type of Firm: Social Good Organizations/Businesses
Definition: Businesses built on innovative solutions and a desire to make the world a better place.
Goal: Maximizing impact in a sustainable way
Kind of Business: A company working to solve global health issues; a company solving specific problems in developing countries; nonprofits with a philanthropic mission.
Capital Providers: Depends on the type and size of company; can run the entire capital continuum
Outcomes: Has the potential to create significant social impact and improve lives
Similarities and differences between entrepreneurial ventures
Small Business vs Scalable Startup vs Social Good organization vs Large Business
Small business vs Scalable Startup
Large Business vs Social good enterprises Similarities
In both cases, some capital providers can be the same like friends, family and personal funds;
Another similarities between them is that they are both companies which generate jobs;
Another similarities between these two ventures is to create significant social impacts and improve lives;
The similarity between these two is that they have a social impact;
Differences
Each of them has a different kind of business, for example Small Business are restaurants, retail stores, with other words these are kind of business that can be hand over from generation to generation, on the other hand, Scalable Startup are kind of companies which produces medical devices or some IT companies which develops software’s or apps and the purpose of these business are to produce a benefit for the foundered investors;
The goal for each of them is different, for large business the principal goal is to employ many people and to generate revenue and profit and the goal for social enterprise is to make the world a better place
An entrepreneur is “one who organizes, manages and assumes the risks of a business or enterprise.” Types of entrepreneurial ventures are:
• Small Businesses ;
• Lifestyle Businesses ;
• Social Good Organisation/Businesses;
• Large Enterprises ;
• Scalable Startup ;
• Second Stage ;
Small Business Entrepreneurship
Small businesses are grocery stores, hairdressers, consultants, travel agents, internet commerce storefronts, carpenters, plumbers, electricians, etc. They are anyone who runs his/her own business. They hire local employees or family. Most are barely profitable. Their definition of success is to feed the family and make a profit, not to take over an industry or build a $100 million business. As they can’t provide the scale to attract venture capital, they fund their businesses via friends/family or small business loans. (Casnocha, 2011) However, the term small business has no single definition, Scarborough & Zimmer (2007) state that the term small business refers to a business that is independently owned and operated, is not dominant in its field of operation, and meets certain standards of size in terms of employees or annual receipts.
Scalable Startup Entrepreneurship
Unlike small business, these entrepreneurs start a company knowing from day one that their vision could change the world. They attract investment from equally crazy financial investors – venture capitalists. They hire the best and the brightest. Their job is to search for a repeatable and scalable business model. When they find it, their focus on scale requires even more venture capital to fuel rapid expansion. (Casnocha, 2011)
Large Company Entrepreneurship
Large companies have finite life cycles. Most grow through sustaining innovation, offering new products that are variants around their core products. Changes in customer tastes, new technologies, legislation, new competitors, etc. can create pressure for more disruptive innovation – requiring large companies to create entirely new products sold into new customers in new markets. Existing companies do this by either acquiring innovative companies or attempting to build a disruptive product inside. Ironically, large company size and culture make disruptive innovation extremely difficult to execute. (Casnocha, 2011)
Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurs are innovators who focus on creating products and services that solve social needs and problems. But unlike scalable startups their goal is to make the world a better place, not to take market share or to create to wealth for the founders. They may be nonprofit, for-profit, or hybrid. (Casnocha, 2011)
M1 Investigate a diverse range of entrepreneurial ventures to demonstrate an understanding of entrepreneurship in both the public and corporate sector.
According to Surbhi (2015), the days are gone, when only the Public Sector was prevalent in the economy. At present, many countries have adopted the policy of Privatisation, through which Private Sector is also gaining importance. For the progress and development of any country, both the sectors must go hand in hand as only one sector cannot lead the country in the path of success. The private sector comprises of business which is owned, managed and controlled by individuals. On the contrary, public sector comprises of various business enterprises owned and managed by Government. Such organizations are either fully or partly owned by the center or state and come under the separate ministry. Some of the public sector organizations are set up by a special act of Parliament.
Comparisons of entrepreneurs as independent entrepreneurs, corporate entrepreneurs and public sector entrepreneurs identified differences and similarities across the dimensions of primary motive, time orientation, skills, attitudes, focus, approaches to risks and failures and courage in the face of ambiguity (Morris & Jones 1999). More recently Kearney, Hisrich & Roche (2009) compared entrepreneurship in public and private organisations, defining public sector entrepreneurship as the process within the public sector organization “that results in innovative activities such as the development of new and existing services, technologies, administrative techniques, and new improved strategies, risk taking and proactivity” (Kearney et al. 2009). These authors also propose that entrepreneurship within the public sector produces superior organizational performance. Other authors who argue that all managers are expected to engage in entrepreneurial management regardless of context (Drucker, 1985; Stevenson & Jarillo, 1990), would expect to find managers in the public sector engaging in entrepreneurial behaviour as both deliberate and emergent strategies (Mintzberg & Waters, 1985). The importance of entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial management in the public sector is an area of growing interest as public sector organisations at all levels face continual tightened resource constraints. In dynamic complex contexts, organisations often need to generate new economic activity for survival. Under conditions of resource constraint, entrepreneurial strategies are potential responses to environments that are open to or tolerant of responsiveness to both opportunistic creation and discovery of opportunities (Alvarez & Barney, 2007).
Private Sector is actually business organizations that owned and run in private individuals.(Heseltine, 2013) There are various types of business in private sector, like Sole Proprietor, Partnership, Limited Companies, Cooperatives, Franchise, and Charities. In spite of various types of these, but actually their aim was almost the same just they did it in different ways. The main reason of all these business is to earn profit and increase their market’s shares. Sole Proprietor is the easiest and oldest type of business that can start with a low cost capital, for example doctors, mechanics, beauticians and etc. This is an individually owned business, it is a type of business which owned and run by one owner. The owner normally is the boss and the worker; they can also employ others or even work in their own business. The owner can make their own decision without discuss with any other partner, it is fast and more efficient. They earn more profits compare to other type of business but oppose this benefits they must also take all the responsible, losses and risks alone. In sole proprietor, there are two type of liability: the unlimited liability and the limited liability. The unlimited liability is more important, the owner’s business assets and his personal assets will be owned by the creditors when the business faces financial losses. Unlike limited liability, the shareholders only liable for the amount that they invested but not their personal owned assets.
University
ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND SMALL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
Lecturer Name: Oguchi Martins Egbujor
Student Name: Marian Bengin
Executive Summary
This study is expected to address the academic enquiry regarding business entrepreneurship and the impact it imparts in the community consequently. The study is also committed to identify how the unique financial and cultural trends are supposed to influence the enterprise. This unit is meant to evaluate the impact of individual occasional factors such as educational and financial background. This course of study enables the novice entrepreneurs to explore and elaborate the scope of the venture types that can be characterized entrepreneurial. This study is destined to determine and assess the central aspects of an entrepreneurial approach in order to analyze the potential impact of small and medium business on the prevalent trend of economy. Moreover, this study conducts an investigation to discern the diverse ambience, which can be cited as stimulants to foster or impediment entrepreneurship.
Table of Content
Introduction:- 4
Task 1 Describing the various ranges of ventures required to consider entrepreneurial 4
Task 2 Describe the various impact that falls on small business in economy 6
Task 3 Discussing the main impacts of entrepreneurial mindset. 8
Task4 Investigate the different ambiences that foster or hinder entrepreneurship. 10
Reference list: 13
Introduction:
The main purpose of this study is the importance of entrepreneurship and small business management. The small business management and entrepreneurship are based upon the learning experience that helps in starting business. Moreover, this provides a rapid experience on the various opportunities that rises in the wide growth of small business. This assist in improving the knowledge of the entrepreneurship and this requires at the time for development of techniques and skills of the management. There is a huge demand to develop the skills of the entrepreneurial at the time of working in the company. There is a huge requirement of the entrepreneur at the time for development of business in small and large scale. The small business management and entrepreneurship assist in developing the skills and techniques of entrepreneurial at the performing of business. This scenario has been focused on the role played by the small entrepreneurial ventures at the time of carrying of business. However, this helps in increasing rate of success in small, medium and large-scale business. There are certain impacts that rise in the economy of small business and required key aspects that is set in entrepreneurial. Various environmental aspects hinder on the entrepreneurship at the time of performing business.
Task 1 Describing the various ranges of ventures required to consider entrepreneurial
P1 Analysis various types of entrepreneurial ventures and describe different types of typology of entrepreneurship.
Entrepreneurship provides the new planning of ideas to start a new setup business in small medium enterprises. Entrepreneur tries to takes all the responsibility at the time of development of business and carrying out of operation in a successive method (Burns, 2011). There is a huge requirement entrepreneurial venture at the time for working in the organizations especially for performing business. The entrepreneurial ventures have been carried out in the performing business in corporate and public sector areas. Entrepreneurial ventures have been focused on providing the proper advice on the services required at the time of working in the early stage. This completely depends on the working of various stage of performing business in the organization. The advisory service rise from entrepreneurial ventures helps to take proper approaches based upon the development of strategy, implementation of various plans and set networking on the specified areas while working in the firm (Do Paço et al. 2015). The main ideas for introducing of entrepreneur are based on business to implement new ideas and planning required tackling on the difficult situation while working in the company. There are different types of entrepreneurship ventures lies and this are follows as-
a)Agricultural entrepreneurs.
b)Trading entrepreneurs.
c) Manufacturing entrepreneurs
There are certain entrepreneurship ventures based upon the uses of technology that includes both the non-technical and technical areas. Moreover, it also includes in the areas of ownership that are based on private, state and joint entrepreneurs at the time of performing business in the company. Entrepreneurship ventures are based on various areas of company while performing business that includes with small, large and medium scale (Down, 2010).
There are various types of typology of entrepreneurship while performing business in the organization. These are as follows:-
a)Entrepreneurial firms:-
This includes with the simple form of company that works based on bigger operational unit constituting with few capable members in the organization. This is the major ideas of entrepreneurs to introduce various ideas to transform into a bigger operational unit (Zahra et al. 2014).
b) Lifestyle firms:-
The entrepreneur tries to implement various planning and ideas to design the lifestyle of the employees in a presentable manner. This encourages the employee at the time of attending of meeting with other organization.
c) Salary-Substitute Entrepreneurs:-
The salary-substitute entrepreneurs tries to implement various ideas to make a proper structure of the salary that is allocated on the employee at the end of month while working in the company.
P2 Describing the differences and similarities that lies in the entrepreneurial ventures
There are various types of entrepreneurial ventures at the time of working in the company. This includes as-
a)Large scale, small scale and medium entrepreneurs:-
These types of entrepreneurs includes in different forms of company while performing business. Moreover, this entrepreneur provides limiting amount of capital required at the working in medium scale firms. In the large-scale company, entrepreneurs’ works in a large-scale production by introducing high risk of performance and creating more amount of profit (Carter and Jones-Evans, 2012).
b) State, joint and private entrepreneurs:-
In the private entrepreneurs, tries to perform duty based on new ideas that help in development of business. The joint entrepreneurs’ lies with the business at the time of working joint ventured with government. The entrepreneurs provide new ideas with the help of government to make execute working of business.
c) Technical and non-technical entrepreneur:-
Thereare two types of entrepreneurs: non-technical and technical process depending upon the working. The technical entrepreneurs try to run business with the help of new technological equipments. This would help the business to increase the rate of productivity by utilizing minimum time (Huang and Knight, 2017). In the non-technical areas entrepreneurs tries to implement various planning and ideas that helps to develop the business.
M1 Missing
D1 Missing
Task 2 Describe the various impact that falls on small business in economy
P3 Discuss micro and small business impact that falls on the economy.
There is a huge important to carry out the small and micro business for the development of economy in U.K. The small and micro business provides the backbone for providing the development of U.K economy. This provides creating certain opportunity in the areas of markets by huge opening of the marketing field for the new start up organization (Griffiths and Wall, 2011). Moreover, micro and small business provides huge opportunity in creating opportunities for employment among the people in U.K. The rise of small-scale business implements new ideas that assist in encouraging the rate of competition with the other companies. In U.K, nearly 99% of business is formed with the help of small and micro business. The opening of new small and micro business contributes the maximum amount of market formation and increase the competition rate of market (Martin and Sunley, 2014). This would increase the economy of the country especially in U.K. The growth of micro and small business reduces the rate of unemployment among the people of U.K. The minimum rate of employment in the small medium enterprises contributes nearly about 14.6 million among which 50% belongs to the private companies in U.K. Most importantly, at the time of starting of small business, there requires employee contributing both skilled and unskilled staffs. However, the small and micro business is less complex as compared with medium business. Hence, the managements find it easier to handle the small business and thus increase the rate of production of the company. The nearly turnover of small medium enterprises lies of about £1.7 trillion and this contributes among the private companies of about 46%. The high production would certainly raise the profit of the firm, thus increasing the economy of U.K. Moreover, the growth of small and micro business increases the growth of business and this leads to increase the economy of the country in U.K (Iacoviello and Pavan, 2013). The small and micro business industry can develop the economy with the help of exporting the products in other countries. In U.K, there are nearly 1.2 million people working to develop the business and nearly 3.9 million people are non-employing at the time of performing business. In order to increase the growth of small and micro business, the management has to keep in mind certain factors and this further follows as-
a) The small and micro business needs to improve the quality of products and services.
b) The small business industry needs to keep the existing consumer as well as new consumers while performing business.
c) Moreover, the industry needs to reduce the cost of the products and needs to fulfill the demand of the customers.
d) The small business needs to sharpen the techniques and process of business.
This includes all the process that help the small and micro business industry to develop the high factors of economy.
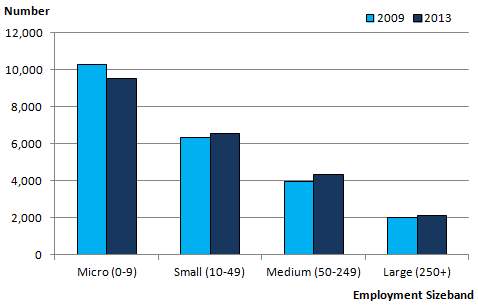
Figure 1: Impact of Small and Medium enterprises on economy
(Source: Piperopoulos and Dimov, 2015)
P4 Explaining the importance of small business and describe the startup growth of social economy:
The small-scale business has been provided as the backbone for the development of economy in U.K. Moreover, small business has contributed a major place by providing employment among the people of U.K. The small business provides various impacts in the areas of economy that includes in national, regional and local level by contributing the better service of the products. This could be seen at the time of exporting of the items in various regions of the countries. Moreover, the small company constantly contributes the higher rate of growth and new creativity among the communities (Eid and El-Gohary, 2013). The small and medium enterprises provide important resources and help to carry out the exact process of the business to function accordingly among large industry.
This is the main important points of carrying business in the small-scale industry in U.K.
There is an immense opportunities for the new start up business in the country of U.K. Moreover, there would enough opportunity to obtain both skill and unskilled labor that are suitable to carry out the business. The new start up business would develop the economy of the country of U.K. Moreover, the start up business provides new products launching that reduces the demand of customer. The new start up business reduces the rate of unemployment among the people. The new starting of business would increase the profit at the time of exporting of products in various countries and thus higher the growth of economy in various levels (Hallegatte, 2014). There is a high necessity to develop the new start up business for increasing the economy in U.K.
Task 3 Discussing the main impacts of entrepreneurial mindset
P5 Describing the main characteristics of skills and traits of successful entrepreneurs that differentiate with the managers of business.
There are various characteristics of the successful entrepreneurs at the time for performing business as compared with the managers of the organization. This characteristic provides the main skills, traits and motivation that drive the entrepreneurs to become more successful for the future aspects (DuvalCouetil, 2013). Entrepreneurs focus on the certain areas that helps them to become more successful and further assists them to carry the business in the long-term aspects. These are as followed as-
a)Proper planning:-
The proper planning is the fundamental areas that need to be focused by the entrepreneurs at the time of performing business. Moreover, the planning includes the capital, time etc that helps in managing of business properly. The proper planning helps to tackle of difficult situation that rise at the time of performing business.
b) Managing of Capital:-
This requires managing the profit at the time of rising of entrepreneurial ventures. There is a high necessity to manage the capital, as this is a limited resources and needs to be spent wisely by the entrepreneurs. The successful entrepreneur’s tries to manage the money and makes proper planning to utilize it for present and future usage. In order to carry out the business in a successive mode, there is a high necessity to manage the money to increase the development of business.
c) Ability to take risk:-
Entrepreneurs need a high ability to tackle all the upcoming situation of risk that rises at the time of performing business. Moreover, the entrepreneurs need to evaluate the risk for long term running of business in the present and future aspects (Purzer et al. 2016). In order to reduce the risk, entrepreneurs need to make proper planning and execute various ideas to tackle the situations of risk that rises while performing business.
d)Motivation and passion:-
In order to become more successful of entrepreneurs, there is a high necessity to follow the passion and needs to provide motivation among the employee at the time for performing business. The motivation and passion would help in determining the success in entrepreneurial ventures. The proper set passion and motivational spirit helps to become more successful among the entrepreneurs.
e)Hard working:-
The hard working, self-belief helps the entrepreneurs to become more successful at the time of performing business. The entrepreneurs need to provide high dedication and might focus on the working and this helps to become more successful.
P6 Analyzing the personality of entrepreneurial that reflects with the mindset and motivation
The entrepreneurial personality highly reflects the entrepreneurial mindset and motivation at the time of performing business. There is a high requirement to reflect the entrepreneurial motivation and mindset. The entrepreneurs need to reflect the positive motivation and mindset while performing business in the organization (Kuratko et al. 2015). Moreover, the positive mindset made by the entrepreneurs helps to complete the business properly and hence helps to achieve the success at the time of performing business. The good working of entrepreneurs reflects on the positive working upon employees. In order to carry out the business effectively there is a high necessity to maintain the performance of the staff to get better performance. The personality of entrepreneurs plays a positive role at that creates a better mindset among the employee to achieve better performance. Moreover, there is a high necessity to maintain the positive behavior of the entrepreneurs at the time of working in the organization. The entrepreneurs needs to focus on creating high motivation among the employees at the time of working as the staff members belongs the main pillar for making of high production of business (Renko et al. 2015). The positive behavior of entrepreneurs helps to make a positive mindset among the employees at the time of performing business.
Task4 Investigate the different ambiences that foster or hinder entrepreneurship.
P7 Investigating the ability of context and experience to foster or hinder entrepreneurship supported by relevant examples
The principal purpose of entrepreneurship is to discern the entrepreneurial occasion and eventually explore the opportunities embedded in it. The ability to evaluate and exploit information can be considered as one of the crucial traits an entrepreneur must possess along with a sincere vigilance which enables the entrepreneur to interpret relevant data in some inescapable circumstances (Carraher, 2015). The entrepreneur’s efficiency can be judged on the grounds of prerequisite knowledge which, according to some research scholars, may be derived from educational background, individual intellect and previous workplace realizations, or may be processed from the empirical perception of the domain (Ramadani et al. 2015). The desired personality characteristics of an entrepreneur can be summarized into three broad traits which is termed as ‘Big Three’ by several scholars of this field and they are Need for Achievement, Locus of Command and Risk-taking Propensity respectively (The other approaches in varying dimensions of traits are excluded). The Need for Achievement can be expressed as a sustainable trait, which is obtained from aiming and accomplishing self-declared tasks of higher levels of merit. Though this trait is usually conceptualized as a stable one, recent articles suggest that the trait evolves in accordance with the advancement of information gain. Moreover, efficient entrepreneurs usually seek excellence-intensive occasions, which are typically aligned with complicated liabilities, moderate risk-taking, prudent anticipation of business performances and potential possibilities. In this aspect, achievement of challenging business pursuit’s turns out is more satisfactory as compared to financial gain to a certain section of entrepreneurs. The theory of locus control introduces several perspectives at the entrepreneur’s ability to process occasional information in order to analyze the social context. The locus of command is a potent index of business expectations and success, which can be classified into internal and external of an individual (Karatas Ozkan et al. 2014). Owner and managers of an enterprise typically exercises a profound internal locus of command as it was integrally attached with entrepreneurial features where the collaboration reflects considerable innovations having more potential and discretion. The external locus of command, whereas, can be considered as an avowal to passivity since it hinders academic pursuits and actions mostly rely on chances or destiny. Risk-taking can be reckoned as a significant feature since it distinguishes non -entrepreneurs and managers from entrepreneurs. The ability of the entrepreneur to calculate the assigned risks depends on the age, motivation, and prevalent business experiences where they exploit the risks as stimuli of their business venture. Most significantly, the risk-taking propensity is associated with need for achievement where the risks determine the capability of the entrepreneur to deal with improvised decisions (Piperopoulos and Dimov, 2015). Some of the decadent civilizations reflect a regressive attitude towards the essence of entrepreneurship since they were conditioned to share their earned wealth among the members of the community and family instead of enjoying it. There are simulating studies, which concludes cultural and social reinforcement as cardinal factors for ‘need achievement’ by altering the conventional factors such as parental influence.
Conclusion:
It has been concluded that there is a high requirements to maintain a proper entrepreneurs at the time of performing business in small medium or large industry. Various ventureslie on the entrepreneurship at the time of performing business. Moreover, the entrepreneurs provide the exact planning and ideas at the time of performance of business. In this assignment, it has been also concluded that there is a high necessity to carry out the small and micro business. This helps in the increasing the working of business and further assist in the development of economy. It has been concluded that there is a high aspects to make the entrepreneurial mindset at the time of performing business. It has been concluded that there is a high requirements to manage the entrepreneurship and the management of small business. It has been also concluded that there is a necessity to maintain the proper behavior of entrepreneurs. This provides the positive impacts at the time of working and hence provides motivation among the staff. It has been concluded that there is necessity to hinder the various impacts of entrepreneurship that lies with environmental factors.
Reference list:
Burns, P (2011) Entrepreneurship and Small Business. 3rd Ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan.
Carraher, S.M. and Paridon, T.J., 2015. Entrepreneurship journal rankings across the discipline. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 19(2), pp.89-98.
Carter, S. and Jones-Evans, D. (2012) Enterprise and Small Business: Principles, Practice and Policy. London: Pearson.
Do Paço, A., Ferreira, J.M., Raposo, M., Rodrigues, R.G. and Dinis, A., 2015. Entrepreneurial intentions: is education enough?. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 11(1), p.57.
Down, S. (2010) Enterprise, Entrepreneurship and Small Business. London: Sage.
Duval‐Couetil, N., 2013. Assessing the impact of entrepreneurship education programs: Challenges and approaches. Journal of Small Business Management, 51(3), pp.394-409.
Eid, R. and El-Gohary, H., 2013. The impact of E-marketing use on small business enterprises’ marketing success. The Service Industries Journal, 33(1), pp.31-50.
Griffiths, A. and Wall, S. (2011) Economics for Business and Management. 3rd Ed. Harlow: Pearson.
Hallegatte, S., 2014. Economic Resilience: definition and measurement. Browser Download This Paper.
Huang, L. and Knight, A.P., 2017. Resources and relationships in entrepreneurship: an exchange theory of the development and effects of the entrepreneur-investor relationship. Academy of Management Review, 42(1), pp.80-102.
Iacoviello, M. and Pavan, M., 2013. Housing and debt over the life cycle and over the business cycle. Journal of Monetary Economics, 60(2), pp.221-238.
Karatas‐Ozkan, M., Anderson, A.R., Fayolle, A., Howells, J. and Condor, R., 2014. Understanding entrepreneurship: challenging dominant perspectives and theorizing entrepreneurship through new postpositivist epistemologies. Journal of Small Business Management, 52(4), pp.589-593.
Kuratko, D.F., Morris, M.H. and Schindehutte, M., 2015. Understanding the dynamics of entrepreneurship through framework approaches. Small Business Economics, 45(1), p.1.
Martin, R. and Sunley, P., 2014. On the notion of regional economic resilience: conceptualization and explanation. Journal of Economic Geography, 15(1), pp.1-42.
Piperopoulos, P. and Dimov, D., 2015. Burst bubbles or build steam? Entrepreneurship education, entrepreneurial self‐efficacy, and entrepreneurial intentions. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(4), pp.970-985.
Purzer, S., Fila, N. and Nataraja, K., 2016. Evaluation of Current Assessment Methods in Engineering Entrepreneurship Education. Advances in Engineering Education, 5(1), p.n1.
Ramadani, V., Dana, L.P., Ratten, V. and Tahiri, S., 2015. The context of Islamic entrepreneurship and business: Concept, principles and perspectives. International Journal of Business and Globalisation, 15(3), pp.244-261.
Renko, M., El Tarabishy, A., Carsrud, A.L. and Brännback, M., 2015. Understanding and measuring entrepreneurial leadership style. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(1), pp.54-74.
Zahra, S.A., Wright, M. and Abdelgawad, S.G., 2014. Contextualization and the advancement of entrepreneurship research. International Small Business Journal, 32(5), pp.479-500.

